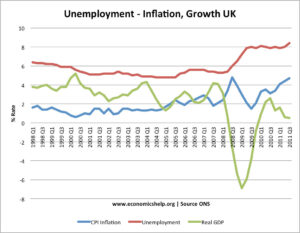
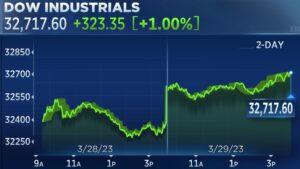
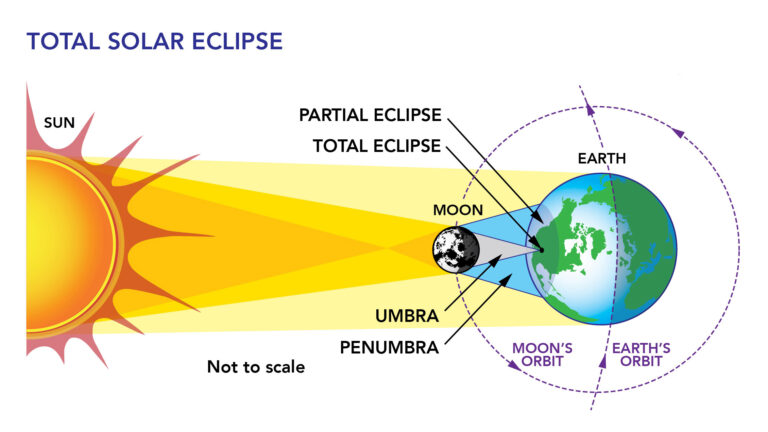
Introduction to Interstellar Comet 3I/Atlas
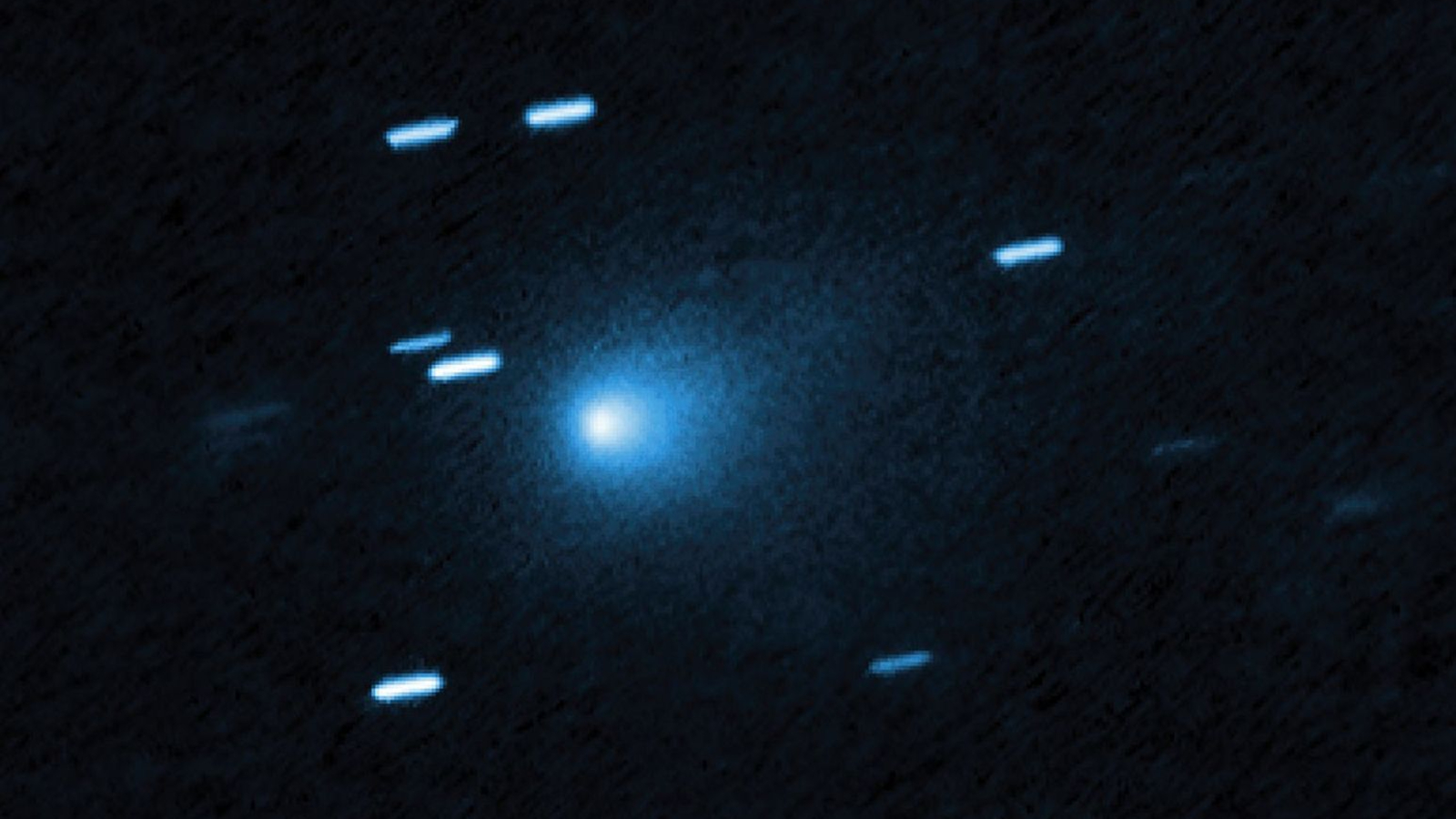
The discovery of interstellar comet 3I/Atlas marks a significant moment in modern astronomy. Unlike comets that originate from our solar system, 3I/Atlas is believed to have come from a distant star system, opening new avenues for understanding the composition and dynamics of interstellar bodies. Its passage through our celestial neighborhood in 2023 has captured the attention of astronomers and space enthusiasts alike, highlighting the importance of ongoing astronomical observations.
Discovery and Characteristics
First identified in December 2019 by the ATLAS (Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System) survey, 3I/Atlas was confirmed as an interstellar object in early 2020, making it the third confirmed interstellar comet after 1I/’Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov. Initial observations indicated that the comet is approximately 1.5 kilometres long and exhibits a unique elongated shape. Its trajectory suggests that the comet will pass closest to the Sun in May 2023, allowing for detailed study from Earth and space-based telescopes.
Scientific Significance
The study of 3I/Atlas provides a rare opportunity to explore materials that have not undergone the processes of our solar system’s formation. Researchers are keen to analyse its composition to understand more about the chemistry of other star systems and the materials that can potentially seed life. Observations from various observatories, including Hubble and ground-based telescopes, are focused on capturing images and spectral data of this intriguing comet.
Implications for Future Research
The passage of interstellar objects like 3I/Atlas can inform theories about the formation of solar systems and the dynamics of galactic evolution. As more such comets are discovered, astronomers may establish patterns in their movement and origins. This growing knowledge may lead to advancements in our understanding of exoplanets and the conditions necessary for life beyond Earth.
Conclusion
The interstellar comet 3I/Atlas is more than just a celestial phenomenon; it represents a widening of our horizons in astronomy. With its expected closest approach in May 2023, researchers are eagerly anticipating valuable data that could shed light on the early solar system and beyond. As interest in the cosmos increases, discoveries like 3I/Atlas remind us of the vast and dynamic universe we are a part of, igniting curiosity and inspiring future generations of astronomers and scientists.