Introduction
Bipolar disorder, formerly known as manic-depressive illness, is a mental health condition that significantly impacts millions of people worldwide. The importance of understanding this disorder lies in its complexity and the challenges it presents for diagnosis and treatment. As mental health awareness grows, the need for accurate information about bipolar disorder has become increasingly relevant. This article aims to inform readers about the symptoms, effects, and available treatments for this often-misunderstood condition.
What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder is characterised by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) estimates that approximately 2.8% of adults in the United Kingdom experience bipolar disorder at some point in their lives. These episodes can vary in frequency and intensity, affecting daily life, work, and relationships.
Symptoms
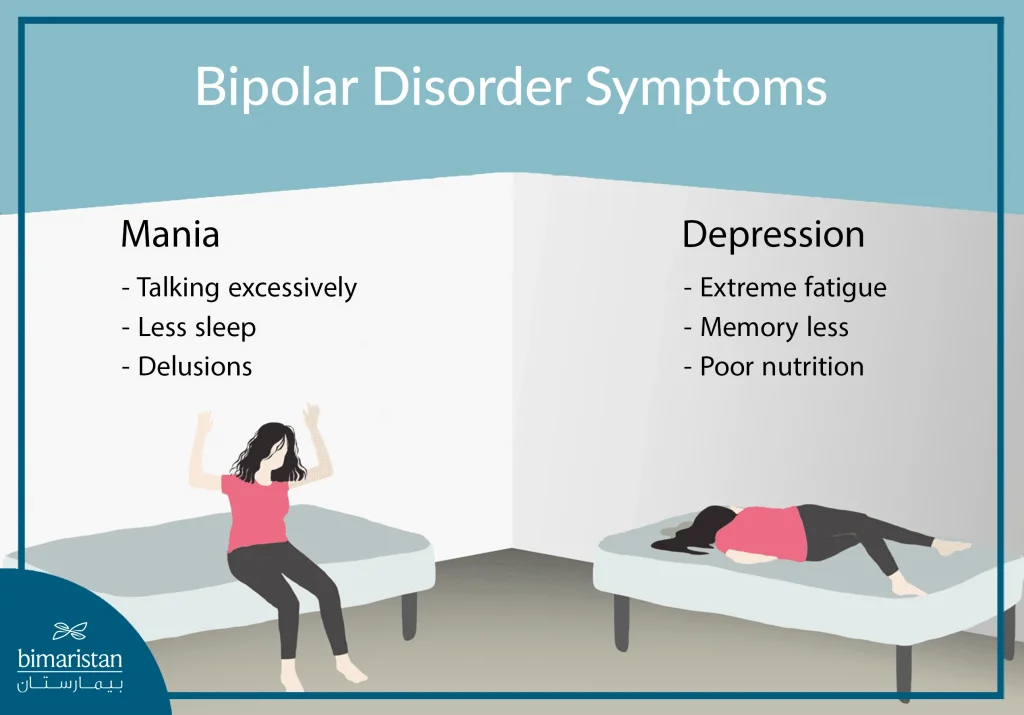
The symptoms of bipolar disorder can differ significantly between individuals, making early detection challenging. Common signs include:
- Manic Episodes: Increased energy, reduced need for sleep, excessive talking, distractibility, racing thoughts, and engaging in risky behaviours.
- Depressive Episodes: Feelings of sadness or hopelessness, fatigue, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite, and thoughts of self-harm.
Current Trends and Research
Recent studies underscore the importance of recognising and diagnosing bipolar disorder early to enhance treatment outcomes. The UK’s National Health Service (NHS) is working to improve access to mental health services, particularly for young adults, who are at a higher risk for developing the condition. Medications, such as mood stabilisers and antipsychotic drugs, are commonly prescribed, alongside psychotherapy, which has been shown to be an effective complementary approach.
Conclusion
In summary, bipolar disorder is a serious and complex mental health condition that requires a multifaceted approach for effective management. Increased awareness and understanding among the public can help reduce stigma and encourage those affected to seek help. By promoting mental health initiatives and ensuring accessible treatment options, society can foster a more supportive environment for individuals living with bipolar disorder. The future looks promising as research continues to develop new therapies, improving the lives of those affected by this condition.