Introduction
Chemical castration is a medical procedure used to significantly reduce libido and sexual activity in individuals, primarily through hormone therapy. This approach plays a crucial role in contemporary society, particularly in the context of crime prevention, criminal justice, and certain medical treatments. Its relevance has surged in discussions surrounding sexual offenders rehabilitation, social justice, and medical ethics.
The Process of Chemical Castration
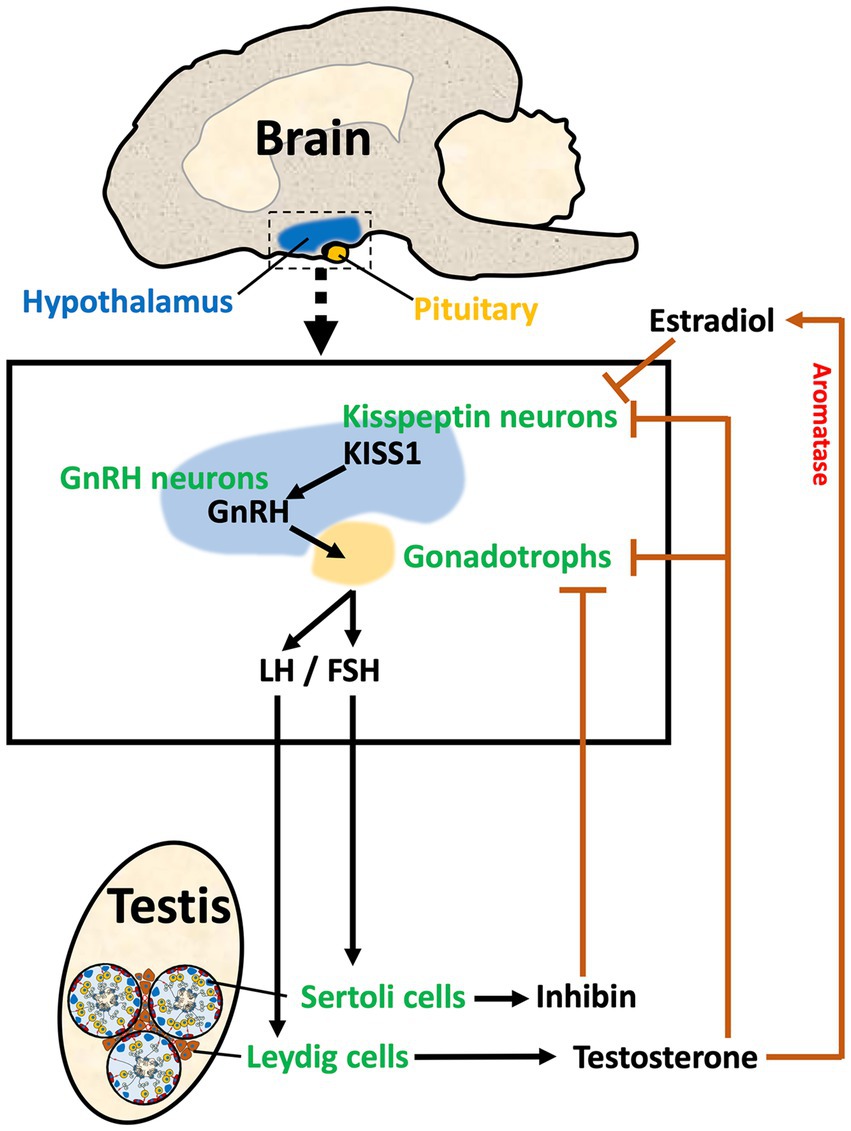
The process involves the use of medication to decrease testosterone levels in the body. Common medications used for chemical castration include GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone) agonists, which work by suppressing the production of testosterone in the testicles. Unlike surgical castration, which is permanent and irreversible, chemical castration is reversible. When the treatment is halted, normal testosterone levels eventually return.
Application in Criminal Justice
In several countries, chemical castration has been legislated as an option for sex offenders as a means to prevent recidivism and protect public safety. In the UK, practices have sparked debates centered around human rights, ethical considerations, and effectiveness. Some studies indicate a reduction in reoffending rates among those who undergo chemical castration, but critics argue that the measures can be seen as punitive and infringe on individual rights, raising concerns about coercion, especially in cases where consent may be questioned.
Chemical Castration in Medical Treatment
Beyond legal implications, chemical castration is also employed in treating hormone-sensitive cancers, such as prostate cancer. Patients undergoing hormone therapy often experience a reduction in symptoms, which can improve their quality of life. However, this treatment comes with potential side effects, including weight gain, mood changes, and osteoporosis, which can impact patients’ overall well-being.
Future Outlook
The conversation around chemical castration is evolving, especially with ongoing advancements in medical research and a greater focus on patient rights. As societies debate the implications of such treatments, the understanding of mental health, rehabilitation, and ethical medical practices will be critiqued and redefined. It emphasizes the importance of tailoring interventions to individual cases rather than applying a one-size-fits-all approach to criminal behavior or medical treatment.
Conclusion
Chemical castration continues to be a contentious topic with significant implications for both the judicial system and medical practices. Its relevance in preventing crime and treating specific medical conditions highlights the complexities of ethical considerations in modern medicine. As society continues to grapple with these issues, ongoing research and discussion will be vital in shaping future policies and practices surrounding chemical castration.