Introduction
The European Union (EU) represents one of the most significant political and economic unions in the world, comprising 27 member states. Established to foster economic cooperation and enhance political stability amongst its members, the EU plays a pivotal role in global affairs. Understanding the diverse realities and contributions of each EU country is crucial for assessing their collective impact on international relations, trade, and policy-making.
Current EU Member States
The EU consists of countries from various regions and cultural backgrounds, including Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and Poland, among others. Each member state brings its unique resources, perspectives, and policies to the union, creating a mosaic of alliances and partnerships conducive to collaborative governance. The latest accession was Croatia, which joined in July 2013, although other nations such as Bulgaria and Romania have been in the EU since 2007 without yet adopting the euro.
Economic Impacts of EU Countries
As of 2023, the EU collectively boasts one of the largest economies globally, with a combined GDP of approximately €15 trillion. Member states contribute to a single market, allowing for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people. This integrated economy enhances trade relationships, leading to significant benefits for national economies. Notably, Germany stands out as the largest economy in the EU, followed by France and Italy.
Challenges and Developments
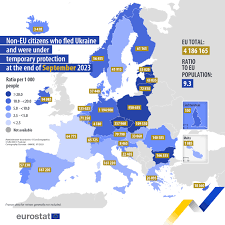
Despite its successes, the EU faces numerous challenges, including political fragmentation, migration issues, and the economic repercussions from the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, the ongoing geopolitical tensions in Eastern Europe, particularly due to the conflict in Ukraine, have prompted renewed discussions on security and defence within the union. As member states navigate these challenges, the unity and resilience of the EU will be tested further.
Conclusion
The relevance of EU countries extends beyond economic cooperation; they are integral to maintaining political peace and stability in Europe and beyond. As the global landscape evolves, the EU’s significance is likely to grow, forefronting issues such as climate change, digital transformation, and international trade. The future of EU countries hinges on pragmatic collaboration and collective solutions to address both internal and external challenges, making it essential for citizens and policymakers alike to stay informed and engaged in EU affairs.