Introduction to West Nile Virus
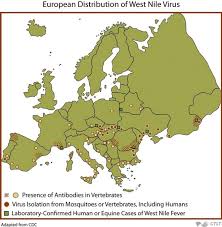
The West Nile Virus (WNV) has become a significant public health concern in many parts of the world, primarily affecting regions in North America, Europe, Africa, and Asia. Identified for the first time in Uganda in 1937, WNV spreads to humans primarily through mosquito bites. With increased awareness of vector-borne diseases following the COVID-19 pandemic, understanding WNV and its implications is more crucial than ever.
Current Events and Outbreaks
As of 2023, several regions, particularly in the United States, have reported a rise in West Nile Virus cases. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), cases have been documented in 30 states, with areas such as California, Texas, and Colorado seeing the highest infection rates. The CDC confirms that, as of late summer 2023, there have been over 600 reported cases this year alone, including 29 fatalities attributed to the virus.
Transmission and Symptoms
WNV is mainly transmitted to humans via the bite of infected mosquitoes, predominantly the Culex species. Notably, the virus can also affect certain birds, which serve as the primary reservoir hosts. While most infected individuals show no symptoms, approximately 20% develop mild symptoms such as fever, headache, and body aches. Severe neurological disease, including encephalitis and meningitis, can occur in less than 1% of infections, particularly affecting the elderly and those with weakened immune systems.
Preventive Measures
Prevention of West Nile Virus relies heavily on controlling mosquito populations and protecting individuals from bites. The CDC recommends wearing long-sleeved shirts and pants, using insect repellent containing DEET, and ensuring door and window screens are intact. Communities are encouraged to eliminate standing water where mosquitoes breed, enhancing public health’s role in combating this endemic issue.
Conclusion: The Future of West Nile Virus Awareness
As we navigate the implications of climate change, it’s essential to remain vigilant about diseases like West Nile Virus. Experts predict that changes in temperature and rainfall patterns may expand the geographical reach of mosquitoes that carry WNV. For readers, awareness and education about the risks, symptoms, and preventive actions can significantly reduce the threat of this virus. Ongoing research and community engagement are vital in protecting public health and mitigating the impact of West Nile Virus across the globe.