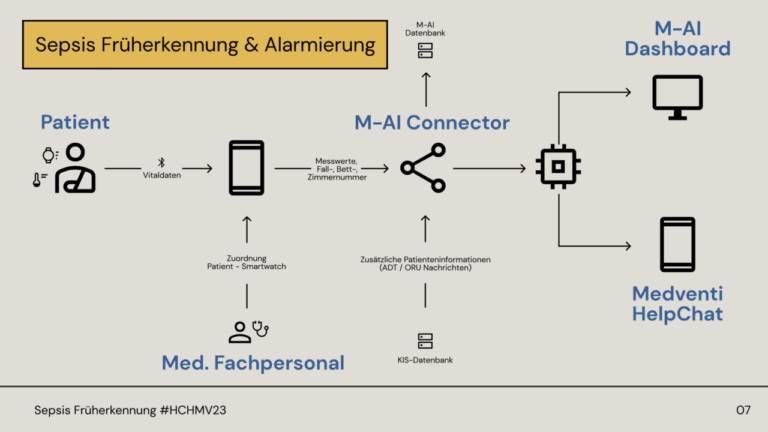
Understanding Cognitive Training and Dementia
Cognitive training encompasses a variety of exercises and activities designed to enhance memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. In recent years, cognitive training has emerged as a significant therapeutic approach in dementia care, which is a growing global health concern affecting millions of individuals.
Importance of Cognitive Training
Dementia affects cognitive functions, leading to challenges in memory, reasoning, and daily activities. As the ageing population increases, so does the prevalence of dementia, with estimates suggesting that over 55 million people are currently living with the condition worldwide. By integrating cognitive training into care plans, healthcare professionals aim to slow the decline in cognitive abilities and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this debilitating condition.
Recent Findings and Studies
Recent studies have highlighted the efficacy of cognitive training programs in mitigating cognitive decline. One notable research project published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society found that seniors who participated in cognitive training showed significant improvements in memory and executive functions compared to those who did not engage in such programs. Additionally, a systematic review conducted in early 2023 supported the idea that individualized cognitive exercises tailored to the interests and needs of dementia patients yielded better outcomes.
Types of Cognitive Training Interventions
Cognitive training interventions can be categorised into computer-based programs, traditional paper and pencil tasks, and engaging group activities. These interventions can include:
- Memory Games: Activities designed to improve recall and recognition.
- Puzzles: Crossword puzzles and sudoku can enhance problem-solving skills.
- Social Engagement: Group activities that promote interaction and cooperation among participants.
Future Directions in Cognitive Training
As technology advances, future research will likely explore the integration of virtual reality and more interactive digital platforms in cognitive training for dementia patients. These innovations may help create more stimulating environments, encouraging participation and engagement. The ongoing pursuit of effective cognitive training methods not only holds promise for improving cognitive function but also offers meaningful social interactions, helping to combat the isolation often felt by those with dementia.
Conclusion
Cognitive training is an important component in dementia care, providing essential pathways to enhance cognitive skills and maintain independence for as long as possible. With continued research and tailored interventions, the future looks promising for dementia patients seeking to improve their cognitive abilities and overall well-being.