Introduction
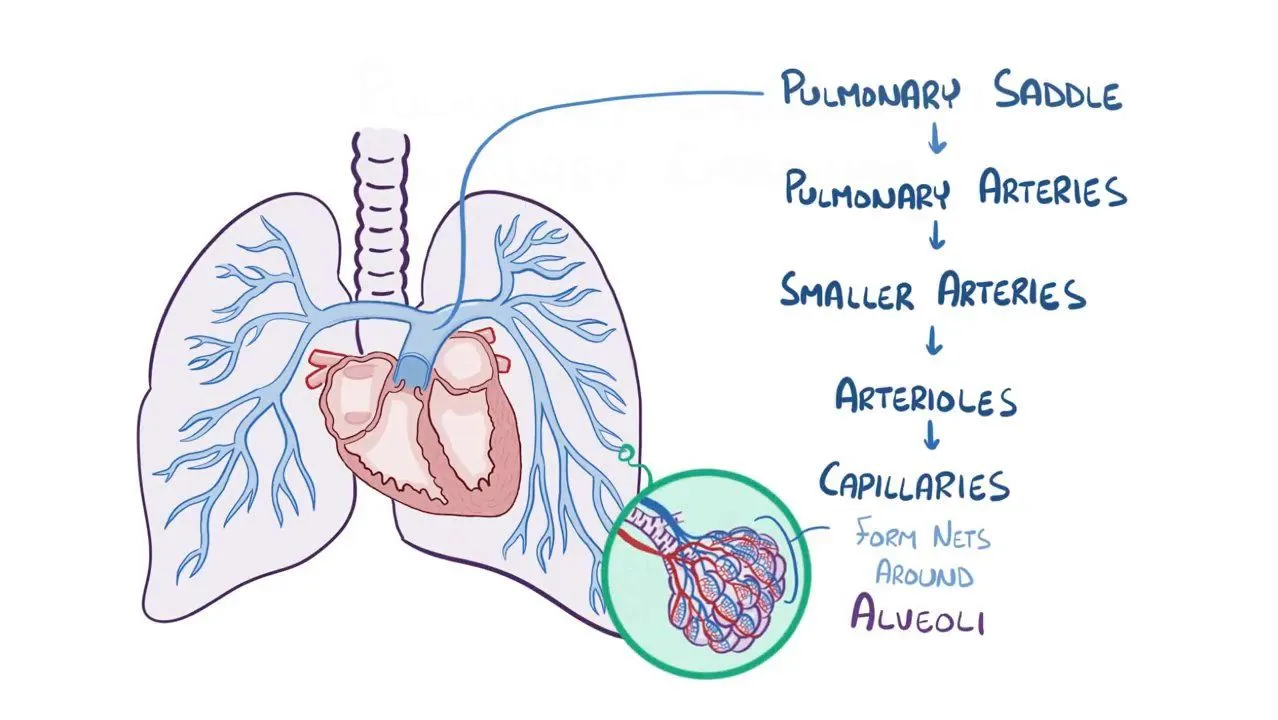
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a life-threatening condition that occurs when a blood clot obstructs a pulmonary artery in the lungs. This blockage can lead to severe consequences, including damage to the lung tissue and compromised oxygenation of the blood. With increasing awareness of vascular health, understanding pulmonary embolism is critical, particularly as risk factors continue to rise globally.
What Causes Pulmonary Embolism?
The primary cause of pulmonary embolism is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), where blood clots form in the deep veins of the legs and then travel to the lungs. Various risk factors increase the likelihood of DVT and subsequently PE, including prolonged immobility, certain medical conditions, obesity, smoking, and recent surgeries. According to the World Health Organization, approximately 1 in 1,000 individuals will experience a PE each year.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism can vary widely. Common symptoms include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain that may feel worse when breathing in, rapid heart rate, and coughing up blood. Because these symptoms can mimic other medical conditions, prompt diagnosis is critical. Diagnostic methods include imaging tests such as CT pulmonary angiography, ventilation-perfusion scans, and blood tests to measure D-dimer levels.
Treatment Options
Immediate treatment for pulmonary embolism usually involves anticoagulants, which help prevent further clotting. In severe cases, thrombolytics may be used to dissolve clots rapidly. In some situations, interventions such as surgical embolectomy or placement of an inferior vena cava filter may be necessary to remove the clot or prevent future clots from reaching the lungs. The choice of treatment often depends on the severity of the case and the patient’s overall health.
Conclusion
Recognising the signs and symptoms of pulmonary embolism is vital for timely treatment and improving outcomes. As we continue to educate the public on the risks and preventive measures, healthcare professionals stress the importance of staying active, managing risk factors, and seeking medical advice when necessary. With advancements in medical research and improving diagnostics, the prognosis for patients with pulmonary embolism can be significantly enhanced.