Introduction
The National Grid is a crucial infrastructure component for the United Kingdom, enabling the transmission of electricity and gas across the nation. As the demand for energy rises, especially in light of climate change and a shift towards renewable energy sources, understanding the National Grid’s operation and challenges has never been more significant. It plays a vital role in maintaining energy security, ensuring that power generation and consumption are balanced, and facilitating the UK’s journey towards net-zero carbon emissions.
Current Developments and Challenges
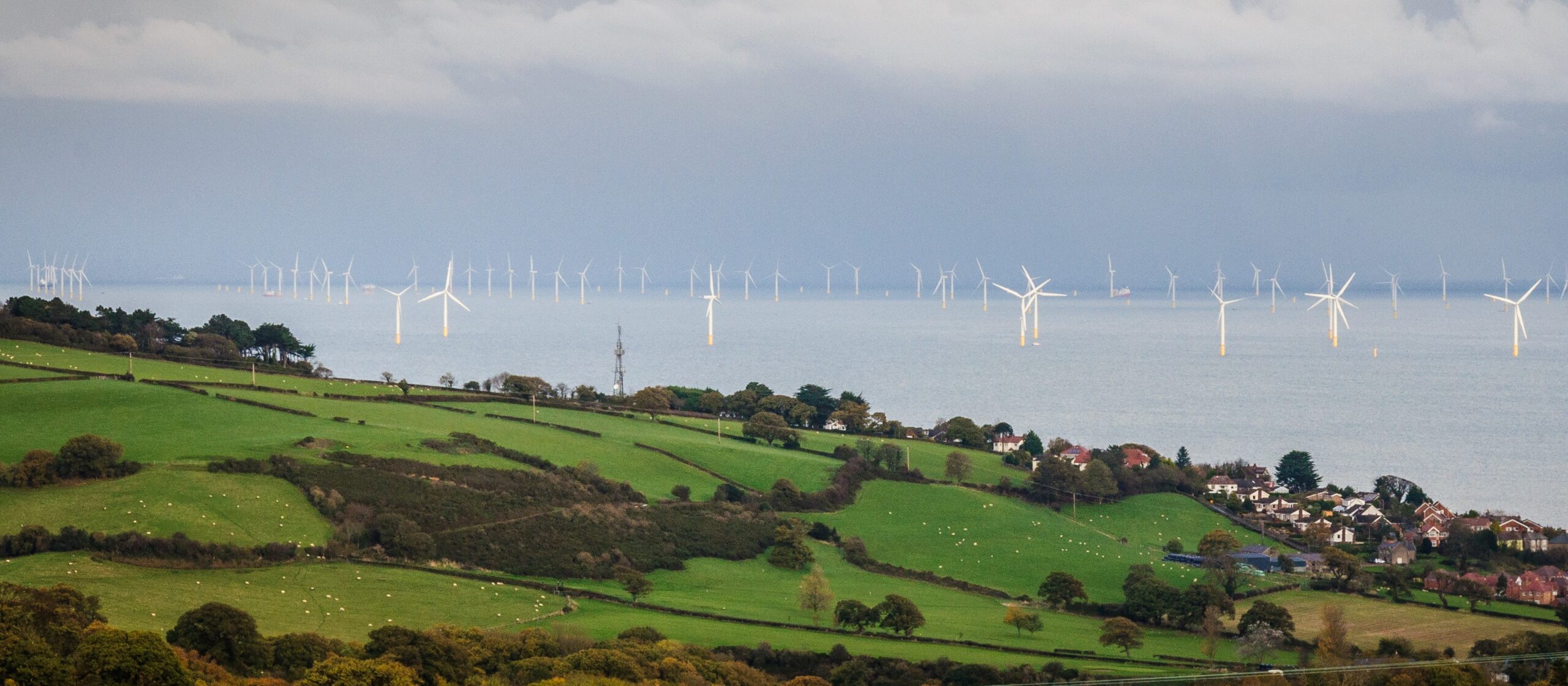
Recently, the National Grid has been under considerable scrutiny due to its expansion efforts to integrate renewable sources like wind and solar into the existing energy mix. In September 2023, the National Grid revealed plans to enhance infrastructure with £10 billion allocated for renewable integration projects over the next decade. These investments are essential as the UK aims to reach 70% electricity generation from renewable sources by 2030.
However, the transition to renewable energy poses several challenges. The shift requires not only technical upgrades to the transmission network but also strategic planning to manage the variability of renewable generation. The National Grid has been implementing new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and smart grid solutions, to improve efficiency and reliability in energy distribution.
Energy Security Concerns
In tandem with these developments, energy security remains a pressing concern. Rising global demand for energy and geopolitical tensions have sparked fears of supply disruptions. Recent reports indicate that the UK government is considering diversifying energy sources and bolstering storage capabilities to mitigate risks. Furthermore, collaborative efforts between the National Grid and energy suppliers aim to create an interconnected energy system, allowing energy sharing across borders, which can provide additional resilience against unexpected shortages.
Conclusion
The National Grid stands at the forefront of the UK’s energy transformation. With ambitious targets for renewable energy integration, it faces a multifaceted challenge of modernisation and enhanced resilience. As investment flows into the grid’s infrastructure, the future looks promising for achieving a sustainable and secure energy system. The ongoing developments within the National Grid are crucial not only for policymakers and energy businesses but also for consumers, as these transformations directly impact energy prices and availability. Observers will be keen to see how these initiatives unfold in the coming years, ultimately shaping the UK’s energy landscape.