Introduction to Ebola Virus
The Ebola virus, a highly fatal disease, remains a significant public health concern, especially in parts of Africa. With its potential to cause widespread outbreaks, understanding the current situation is crucial for global health security.
Recent Outbreaks and Response
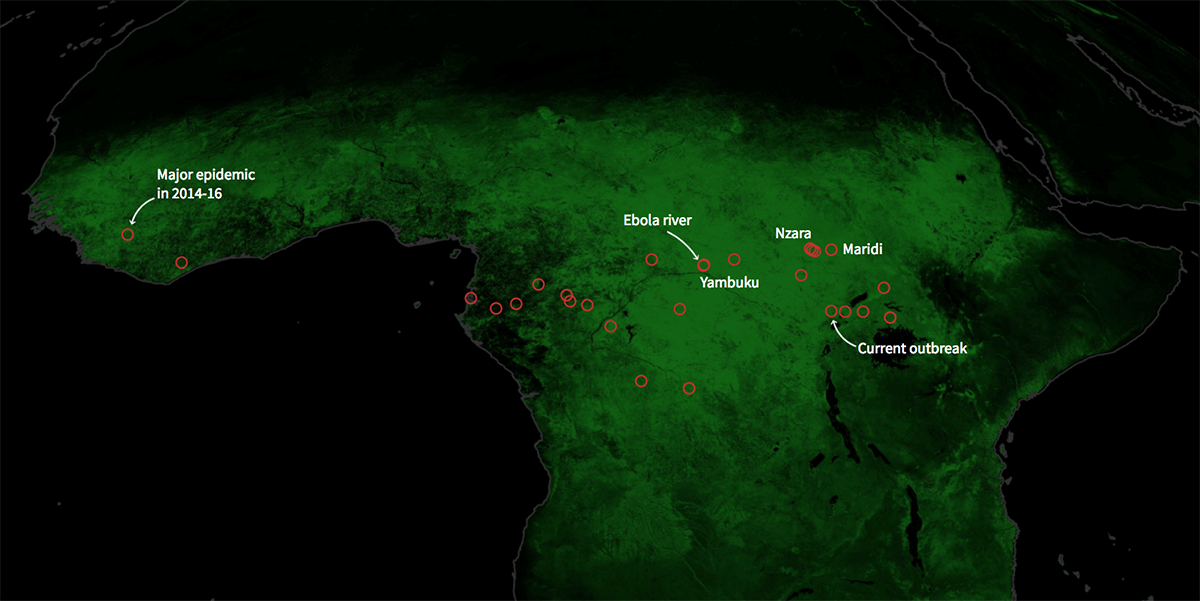
As of October 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported a resurgence of Ebola cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). The most recent outbreak was declared in late September, attributed to the Zaire strain of the virus. As of mid-October, there have been 41 confirmed cases and 15 deaths reported. Health authorities have mobilised resources and initiated containment measures, including contact tracing and vaccination campaigns using the rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine.
Importance of Vaccination and Preparedness
The swift response of health officials emphasizes the importance of preparedness, given the high fatality rates associated with Ebola, which can reach up to 90% in unvaccinated individuals. Vaccination remains a pivotal strategy in controlling outbreaks. The rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine has shown efficacy in previous outbreaks and is a critical tool in mitigating the virus’s spread.
Global Health Challenges
Despite advancements in treatment and prevention, Ebola highlights persistent global health challenges, including insufficient healthcare infrastructure in affected regions, public fears surrounding vaccination, and the need for continuous funding for health initiatives. The ongoing crisis due to the COVID-19 pandemic has also diverted attention and resources from Ebola preparedness, underscoring the importance of a multifaceted approach in tackling various health threats simultaneously.
Conclusion and Future Implications
The situation regarding the Ebola virus demands constant monitoring and international cooperation. With vaccination efforts gaining pace in the DRC, the outlook can improve, but vigilance is essential. Policymakers and health organisations must prioritise resources to not only contain the current outbreak but also enhance long-term health infrastructure to prevent future crises. As Ebola remains a critical public health threat, awareness and preparedness will be crucial in safeguarding communities.