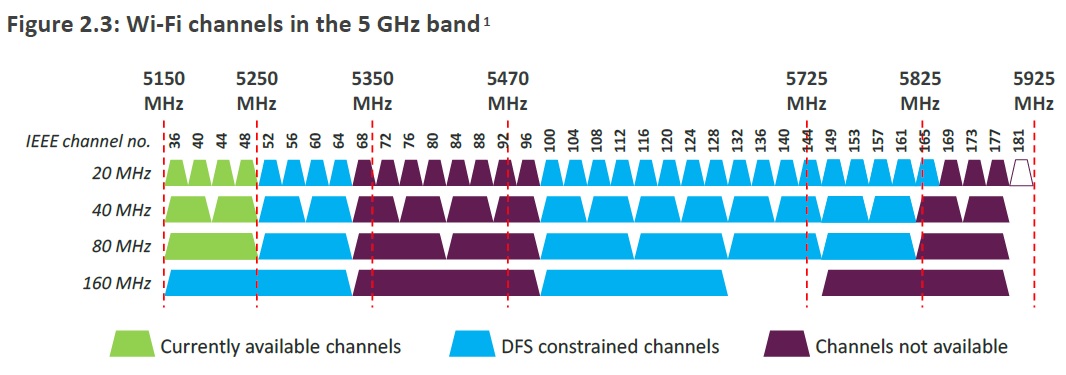
Introduction to Ofcom
Ofcom, the Office of Communications, serves as the UK’s communications regulator, playing a vital role in overseeing a wide array of services including television, radio, telecommunications, and postal services. Established in 2003, this independent agency is essential for maintaining a competitive marketplace, ensuring consumer protection, and fostering innovation in the rapidly evolving communications sector.
Ofcom’s Responsibilities
Ofcom’s responsibilities are multifaceted. It ensures that communications services are available to all, promotes fair competition among providers, and protects consumers from unfair practices. Moreover, Ofcom regulates the content of television and radio broadcasting to uphold standards, prevent discrimination, and protect vulnerable audiences, such as children. In recent years, Ofcom has also expanded its focus to include digital platforms and internet services, addressing the challenges posed by online regulations.
Current Events and Initiatives
In recent weeks, Ofcom has been in the spotlight for its response to the rising concerns around online safety and misinformation. In July 2023, the UK government announced the Online Safety Bill, which escalates Ofcom’s role in regulating social media platforms and streaming services. This legislation aims to hold companies accountable for harmful content and increase transparency regarding user data. As a result, Ofcom has initiated consultations with stakeholders to develop guidelines that will ensure compliance while considering the need for freedom of expression.
Moreover, Ofcom has published a report addressing the state of the UK’s digital communications market, revealing that the demand for higher internet speeds continues to grow. The agency has urged network providers to invest in infrastructure to avoid a digital divide, particularly in rural areas.
The Importance of Ofcom
As the communications landscape continues to shift dramatically, especially with the rise of digital platforms, Ofcom’s role becomes increasingly vital. Its ability to adapt to the emerging challenges of online safety, consumer rights, and infrastructure development is crucial for ensuring that the interests of all users are safeguarded in this wireless future.
Conclusion
With its strategic significance in the realm of communications, Ofcom not only oversees current market conditions but also anticipates the future needs of consumers and providers alike. By navigating the delicate balance between regulation and innovation, Ofcom remains an indispensable part of the UK’s communications framework. Stakeholders from all sides will be watching as the agency continues to expand its influence and adapt to the digital age.