Introduction to Senegal
Senegal, located on the westernmost tip of Africa, is known for its diverse culture, rich heritage, and strategic economic significance. With a population of over 16 million people, it stands out as a beacon of stability in a region often associated with political turbulence. Understanding Senegal’s significance is crucial, especially in the context of ongoing economic development initiatives and cultural preservation.
Cultural Significance
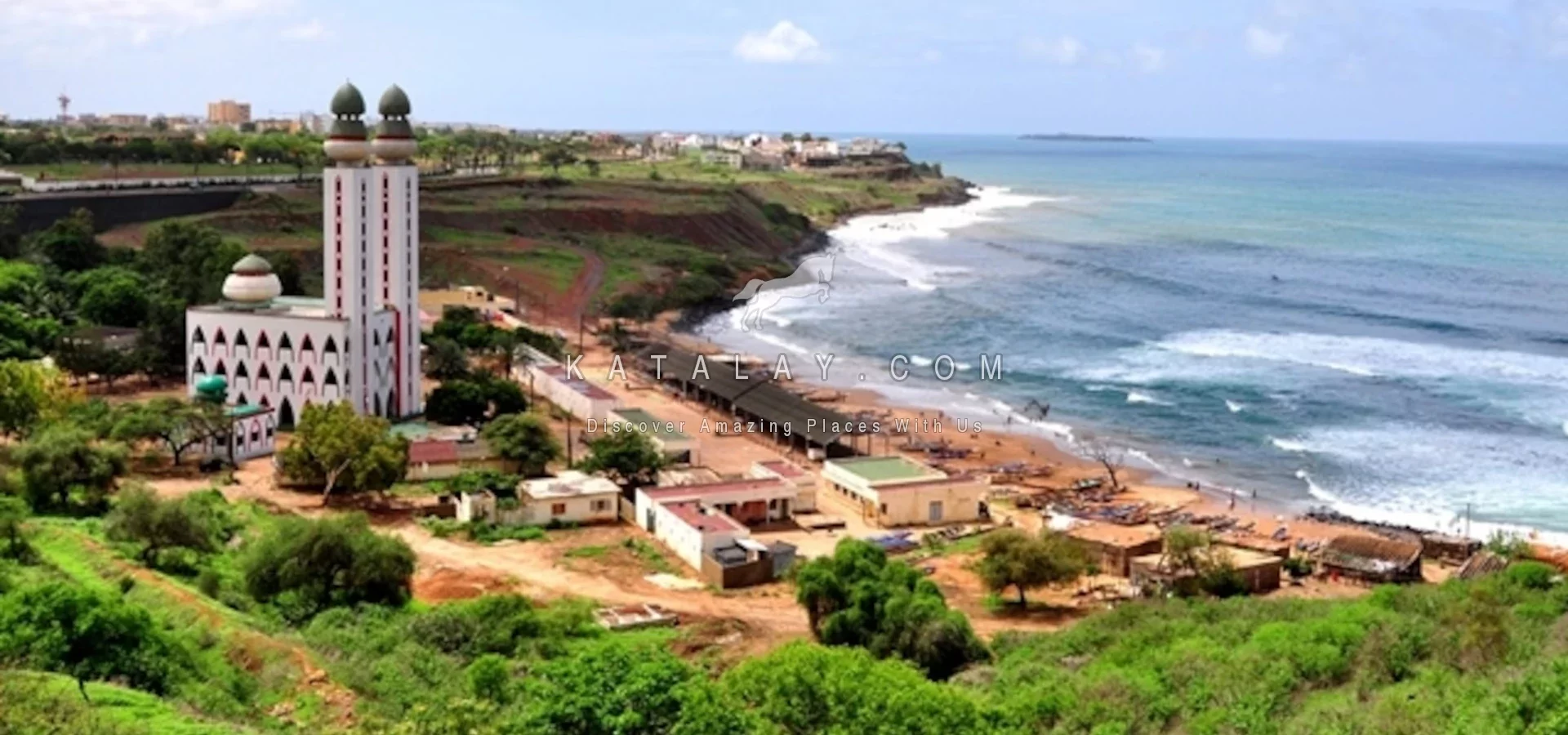
Senegal is home to a multitude of ethnic groups, with the Wolof being the largest. The country’s culture is a tapestry woven from traditional African customs, Islamic practices, and French colonial influences. Senegal’s capital, Dakar, is famous for its lively music scene, particularly the mbalax genre, and hosts numerous festivals celebrating both contemporary and traditional arts.
The vibrant markets, such as Dakar’s Sandaga Market, reflect the daily life of the Senegalese people, making it a popular destination for both locals and tourists. Traditional crafts, including intricate beadwork and textiles, play a significant role in Senegal’s economy, providing livelihoods for many artisans.
Economic Landscape
In recent years, Senegal’s economy has shown remarkable growth, driven by sectors such as agriculture, fisheries, mining, and tourism. The government has initiated several ambitious infrastructure projects, including the Senegal Emerging Plan (PSE), aimed at transforming the economy by attracting foreign investment and promoting sustainable development.
A significant contributor to this growth is the oil and gas sector, with offshore discoveries presenting promising opportunities for revenue generation. According to the Senegalese Ministry of Economy, the country’s GDP is projected to grow by 6% annually over the next few years, largely due to these developments.
Challenges and Opportunities
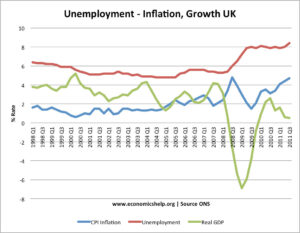
Despite its progress, Senegal faces challenges such as high unemployment rates, particularly among the youth, and regional inequalities in wealth distribution. Addressing these issues is crucial to ensuring inclusive growth. The government, however, is actively working on educational and vocational training programs to equip young people with the skills they need to enter the workforce.
Conclusion
Senegal stands at a pivotal moment in its history, where its rich cultural heritage meets emerging economic opportunities. As the nation continues to develop and modernise, the balance of maintaining its traditional roots while pursuing innovation will be vital. For readers interested in the dynamics of West Africa, Senegal offers a unique glimpse into the potential and challenges faced by a rapidly evolving nation.