Introduction to Phishing
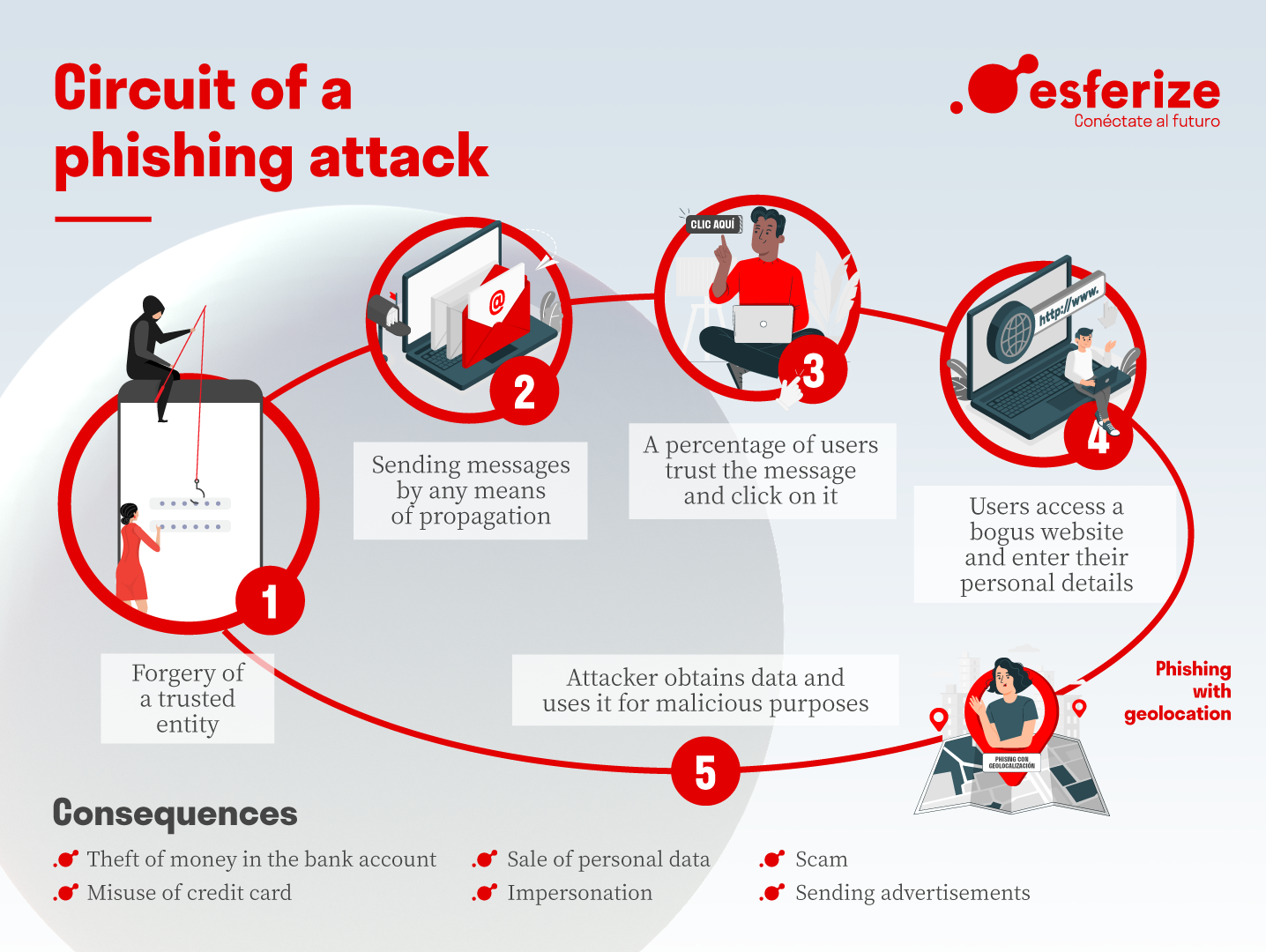
In today’s digital age, cyber threats are an ever-present danger, with phishing emerging as one of the most significant risks. Phishing is a form of cybercrime that involves deceptive techniques used by cybercriminals to obtain sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details. Understanding phishing is crucial for both individuals and organisations to protect themselves against financial loss and identity theft.
How Phishing Works
Phishing typically involves an attacker masquerading as a trustworthy entity in electronic communications. This can come in various forms, including emails, text messages, and advertisements that appear legitimate. For instance, a phishing email might come from what appears to be a reputable bank, encouraging the recipient to click on a link to verify their account information. Unfortunately, this link often leads to a fake website designed to capture the user’s data.
Types of Phishing
There are several types of phishing attacks, including:
- Spear Phishing: A targeted attempt aimed at specific individuals or organisations, often customised to increase success.
- Whaling: A more sophisticated form of phishing targeting high-profile individuals, such as executives.
- Vishing: Voice phishing that involves phone calls, where attackers may impersonate legitimate businesses.
- Smishing: Phishing attempts carried out via SMS texts.
Recent Trends and Statistics
According to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), phishing attempts have dramatically increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, with reports of scams exploiting people’s fears and uncertainties. A report by the Anti-Phishing Working Group noted that phishing attacks rose by 220% in just a few months in 2020. These statistics highlight the need for heightened vigilance among internet users.
Preventive Measures
To guard against phishing, individuals and organisations can take several proactive steps:
- Verify the sender’s email address and be cautious of unsolicited communications.
- Utilise two-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Educate employees and family members about the risks of phishing and how to identify suspicious messages.
- Employ security software to detect and block phishing attempts.
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness
Phishing remains a prevalent threat within the digital landscape, capable of devastating consequences. By understanding what phishing is and how it operates, individuals can take informed steps to shield their sensitive information and maintain their online security. In an increasingly connected world, awareness and education about phishing are vital in fostering a safer online environment for everyone.