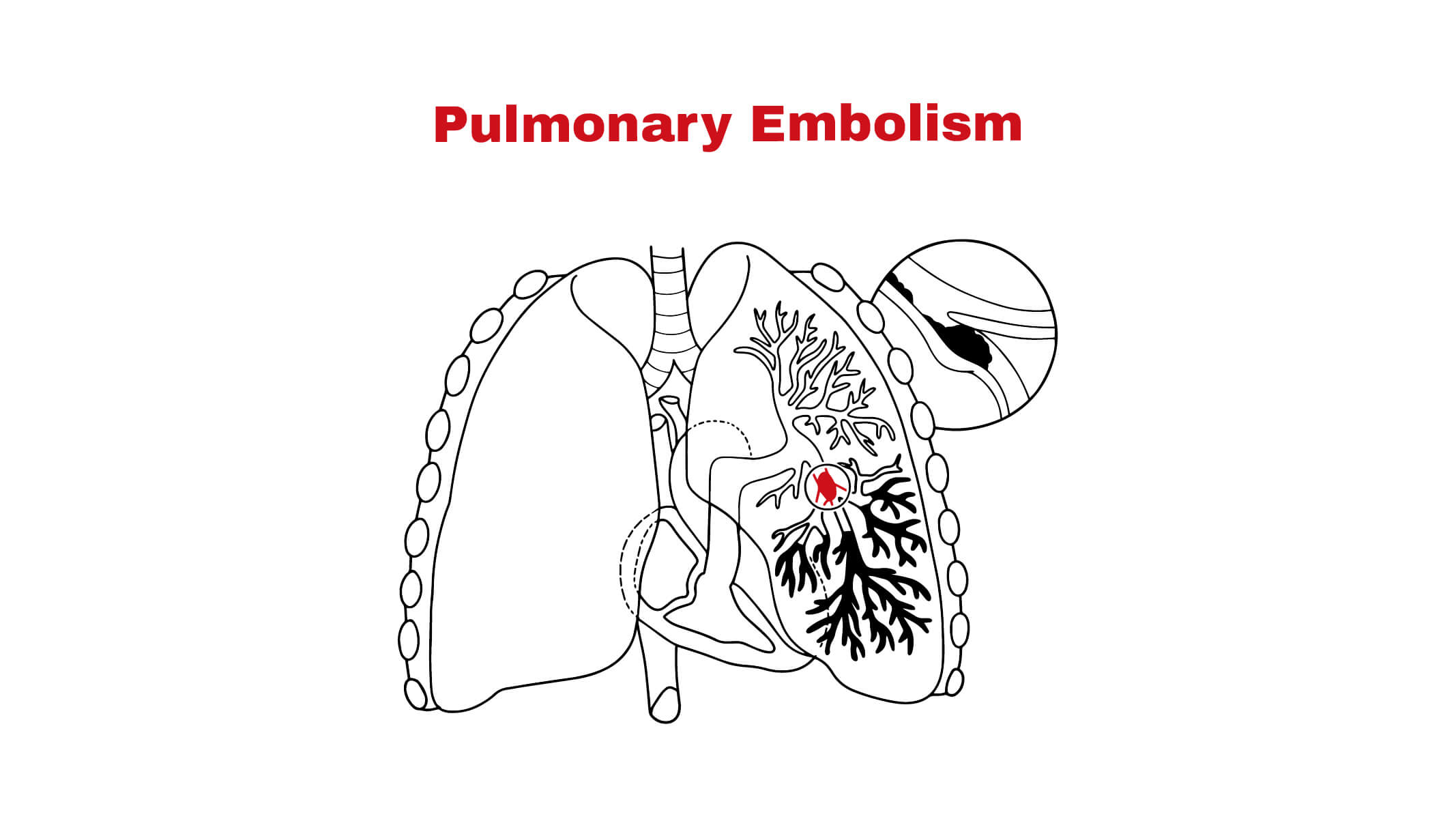
Introduction
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs, blocking a pulmonary artery. This obstruction can lead to severe complications, including respiratory failure and death if not treated promptly. With an estimated 600,000 cases occurring in the United States each year, understanding its symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures is crucial for public health.
What Causes Pulmonary Embolism?
The primary cause of pulmonary embolism is the formation of blood clots, often originating from the deep veins in the legs, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Other factors contributing to PE include prolonged immobility, surgery, some medications, obesity, smoking, and specific medical conditions such as cancer or heart disease. Awareness of these risk factors can aid in early detection and prevention.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism
Recognising the symptoms of pulmonary embolism is vital for early intervention. Common signs include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain that may worsen with deep breathing, a cough that may produce blood, rapid heart rate, and lightheadedness. These symptoms can vary significantly among individuals, making it essential to seek immediate medical attention if they occur.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism typically involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history assessment, and imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT) scans or pulmonary angiography. Treatment usually consists of anticoagulant medications that prevent further clotting, thrombolytics that dissolve existing clots, and sometimes surgical interventions for severe cases. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial factors that improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Conclusion
Understanding pulmonary embolism is essential given its high incidence and potential for serious health consequences. Awareness of the risk factors, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking immediate medical help can significantly reduce the risks associated with this medical emergency. With ongoing research and improved treatment options, the prognosis for patients diagnosed with PE continues to improve, emphasising the importance of education and early intervention in managing this condition effectively.