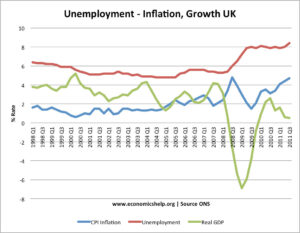
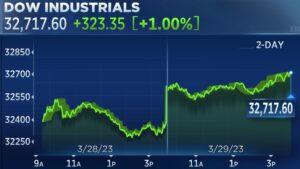
Introduction
The number three has long been regarded as significant across many cultures and disciplines. Its presence is notable in mythology, religion, and philosophy, making it a subject of interest for historians and scholars alike. Understanding the relevance of the number three allows us to appreciate its influence on art, literature, and even scientific theories, shaping our worldview in profound ways.
The Cultural Impact of Three
In many cultures, the number three is often associated with harmony, wisdom, and understanding. For instance, in Christianity, the Holy Trinity embodies the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit, representing a foundational concept in religious teachings. Similar triads can be found in other religions; Buddhism speaks of the Three Jewels, and Hinduism highlights the Trimurti.
Beyond spirituality, three is prevalent in storytelling. The “rule of three” is a principle used in writing and public speaking, suggesting that ideas presented in threes are inherently more humorous, satisfying, and effective. Famous examples include fairy tales like “The Three Little Pigs” and the classic narrative structure of beginning, middle, and end.
Scientific Relevance
In the realm of science, the number three also shows its significance. The three primary colours—red, blue, and yellow—form the foundation of colour theory in art and design. Additionally, in physics, three dimensions (length, width, height) describe the space we inhabit. This multi-faceted presence in various fields only highlights the depth and versatility of the number three.
Conclusion
As we navigate through different cultures and disciplines, the number three remains a powerful symbol of completeness and understanding. Its implications resonate not only in everyday life but also in the philosophy of how we perceive and interact with the world. Moving forward, recognising the importance of such symbols can deepen our appreciation for the rich tapestry of human experience and knowledge.