Introduction
The National Grid plays a pivotal role in the United Kingdom’s energy infrastructure, providing electricity and gas to homes and businesses across the country. As the energy landscape evolves with increasing reliance on renewable sources, understanding the National Grid’s operational framework and its significance becomes essential. This system ensures reliability, energy security, and a reduction in carbon emissions, shaping a sustainable future for the UK.
Current Structure and Functionality
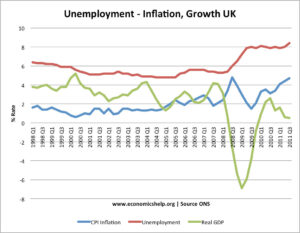
The National Grid is essentially the interconnected network that transmits electricity and gas. Operated primarily by the National Grid Electricity System Operator (ESO), the system balances supply and demand in real-time, ensuring that energy is available whenever it is needed. Currently, the UK has a diverse energy mix, with a push towards increasing the share of renewables such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. Recent statistics from the UK’s Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy indicate that renewables accounted for approximately 48% of total electricity generation in 2023, demonstrating the rapid transition towards a greener energy sector.
Current Events and Developments
In light of recent climate change challenges, the UK’s government has set ambitious targets for net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. The National Grid has been at the forefront of these changes, investing in the enhancement of grid capacity, modernization of infrastructure, and the incorporation of energy storage solutions. Upcoming projects, including the North Sea Wind Plan, aim to significantly expand offshore wind capacity, further aiding in reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, innovative technologies such as smart grids and demand-side response initiatives are being implemented to optimize energy usage and manage peak demand periods effectively.
Conclusion
As the UK navigates the transition to a sustainable energy future, the National Grid is more crucial than ever. Its ability to integrate renewable energy sources, enhance energy efficiency, and ensure supply security will be critical in achieving national climate goals. Stakeholders in the energy sector must continue investing in modern technologies and infrastructure to maintain a resilient energy system that withstands the pressures of climate change and meets growing energy demands. The road ahead is promising; with proactive planning and innovation, the National Grid will be instrumental in fostering a cleaner, greener future.