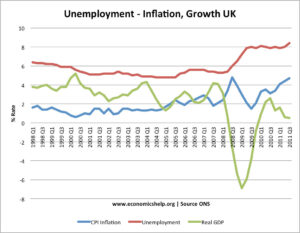
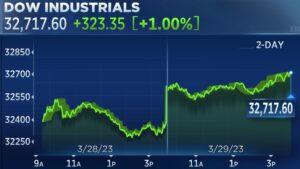
Introduction
Vitamin D, often referred to as the ‘sunshine vitamin’, plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. Its significance has surged recently, especially in light of research linking vitamin D levels with numerous health outcomes, including bone health, immune function, and chronic disease prevention. This topic becomes even more relevant as more people engage in indoor lifestyles, which may lead to inadequate sunlight exposure and, consequently, lower vitamin D levels.
The Role of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is not merely a vitamin; it functions as a hormone that regulates calcium and phosphorus in the body, essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth. The two primary forms of vitamin D are D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol), with the latter typically being more effective at raising vitamin D levels in the blood.
Sources of Vitamin D
There are several ways to obtain vitamin D:
- Sunlight: The body produces vitamin D when the skin is exposed to sunlight, particularly UVB rays. Just 15-30 minutes of sun exposure several times a week can typically fulfill an individual’s requirements.
- Food: Vitamin D can be found in various foods, such as fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), fish liver oils, egg yolks, and fortified products, including certain milk and cereals.
- Supplements: For individuals at risk of deficiency, especially those with limited sun exposure or dietary intake, supplements may be necessary. Recent studies suggest that individuals may require higher doses than previously recommended, particularly during winter months when sunlight is scarce.
Recent Research Findings
A growing body of research underlines the health implications of maintaining optimal vitamin D levels. A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition in 2023 outlined a potential correlation between sufficient vitamin D levels and a lower risk of respiratory infections, including COVID-19. Additional studies continue to explore its role in mental health, with emerging evidence suggesting that adequate levels of vitamin D may combat feelings of depression and anxiety.
Conclusion
As public awareness of the importance of vitamin D increases, health professionals encourage regular monitoring of vitamin D levels, particularly in populations at risk of deficiency. With the potential benefits extending across various health domains, ensuring adequate vitamin D intake—whether through sunlight, diet, or supplements—might significantly contribute to overall health and well-being. Future studies will continue to provide critical insights into the optimal levels of this essential nutrient and its impact on both physical and mental health.