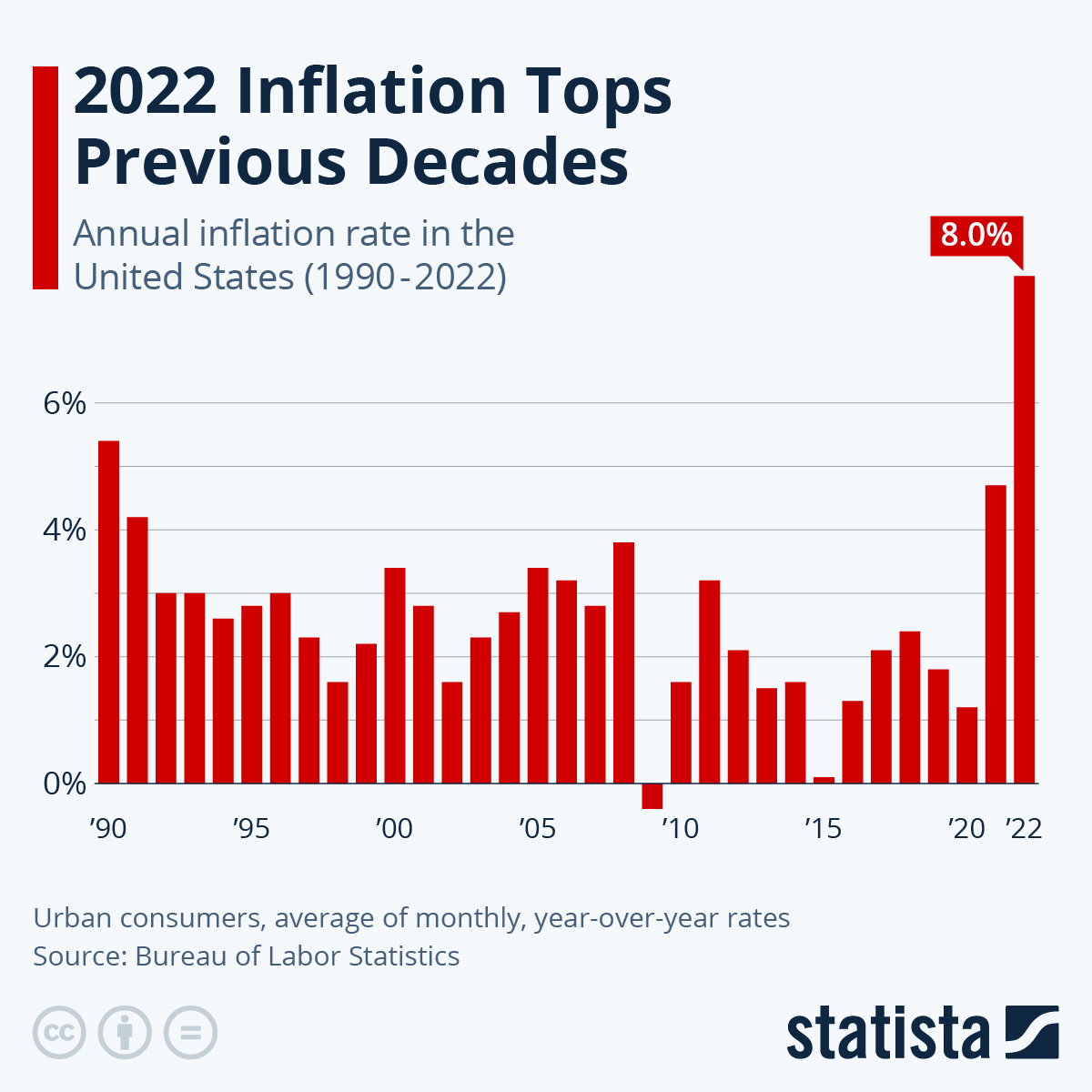
Understanding the US Inflation Rate
The US inflation rate has become an increasingly critical topic in recent months, as fluctuating prices impact everyday consumers and economic policies. With the inflation rate reaching levels unseen in decades, it is essential to examine the factors contributing to this rise and its implications for the economy.
Recent Developments
As of September 2023, the US inflation rate stood at 3.7%, showing a slight increase from the previous month’s 3.5%. This rate is a significant decline from the peak of 9.1% recorded in June 2022, but still poses challenges for policymakers and households alike. The primary drivers behind this uptick include factors such as higher energy prices, persistent supply chain disruptions, and increased consumer demand.
Energy Prices
One of the most substantial contributors to the current inflation rate is the rise in energy prices, particularly for gasoline. Recent data indicates that gas prices have surged by over 10% in the past month, driven by geopolitical tensions and OPEC production cuts. These increases spill over into various sectors, affecting transportation costs, and, consequently, prices of goods and services across the board.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain issues continue to create bottlenecks, impacting the availability of essential goods. Firms are still grappling with the aftereffects of global shipping delays and shortages in raw materials. Consequently, these disruptions hinder production timelines, prompting manufacturers to raise prices to maintain profit margins.
Consumer Demand
The demand side of the equation remains strong due to a robust job market and wage growth that has outpaced inflation in many sectors. However, this high demand, coupled with supply issues, intensifies inflationary pressures and complicates the Federal Reserve’s efforts to manage the economy.
Implications for Future Policy
The Federal Reserve has been taking a proactive approach to combat inflation by implementing interest rate hikes. In recent meetings, officials signalled the possibility of another rate hike, which could occur before the end of the year. These measures aim to curb borrowing and spending, thereby cooling inflation. However, critics argue that tightening monetary policy too quickly may risk pushing the economy into a recession.
Conclusion
As the US inflation rate fluctuates, it remains a focus for policymakers, financial markets, and everyday consumers. Understanding the drivers behind inflation and its implications is crucial for navigating the current economic landscape. Going forward, it is essential to monitor both the inflation rate and the Federal Reserve’s actions, as these will have significant ramifications for the broader economy and individual financial well-being.