Introduction
As digital transformation continues to shape the way governments operate, the introduction of digital ID cards is emerging as a vital innovation. These digital identifiers promise to enhance security, streamline access to public services, and improve the overall efficiency of governmental interactions with citizens. In the UK, the movement towards implementing digital ID cards is not just a technological advancement but a necessary response to the evolving digital landscape.
Current Developments
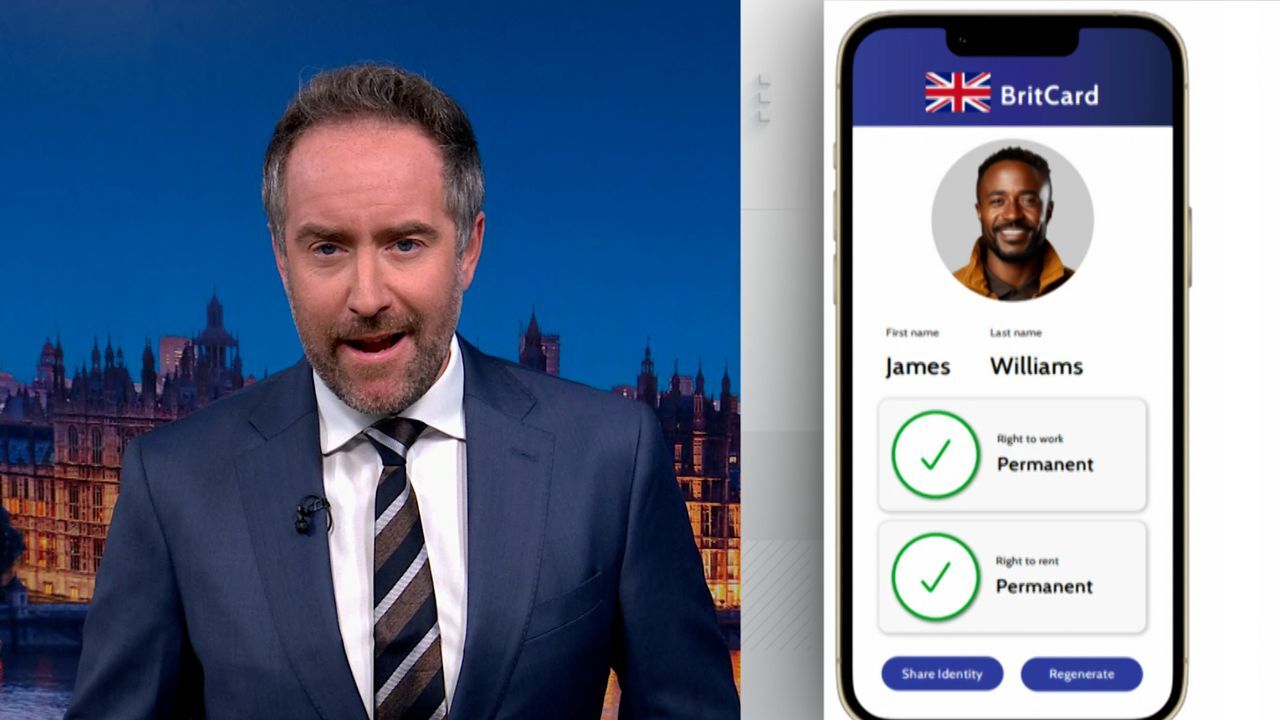
In recent months, the UK government has made strides towards the implementation of digital ID cards. Reports indicate that the Home Office is planning trials for a digital identity verification system by 2024. This system aims to allow citizens to prove their identity through a secure app on their smartphones, eliminating the need for physical documentation such as passports or driving licenses in various contexts.
Currently, a pilot scheme in Northern Ireland has been launched, offering digital ID cards to specific groups, including immigrants and vulnerable populations. These cards will enable users to access essential services, including healthcare and social security, without the cumbersome process of manual verification. If successful, this initiative could pave the way for broader use across the UK.
Benefits and Challenges
The benefits of digital ID cards are significant. They offer enhanced security through biometric data, reducing instances of identity theft and fraud. Moreover, they facilitate a more user-friendly experience, enabling quick access to government services through authentication technologies such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning.
However, implementing digital ID cards is not without its challenges. Concerns about data privacy and security are paramount. Citizens need assurances that their personal information will remain confidential and protected from potential breaches. Additionally, there are discussions around digital literacy and the need to ensure that all demographics can access and utilise these new technologies effectively.
Conclusion
The shift towards digital ID cards represents a significant advancement in governmental service delivery in the UK. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential benefits of enhanced security and streamlined access to services cannot be understated. As the pilot programs roll out and feedback is gathered, stakeholders must remain vigilant in addressing privacy concerns while fostering inclusivity in access to digital identities. The future of government interaction may well depend on how successfully these initiatives can be implemented and embraced by society.