Introduction
The Bank of England base rate is a crucial component of the United Kingdom’s monetary policy, influencing the economy by affecting borrowing and lending rates. This rate, set by the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), has significant implications for individuals, businesses, and overall economic stability. In light of recent inflationary pressures and economic challenges, the base rate’s current standing is more relevant than ever.
Recent Developments
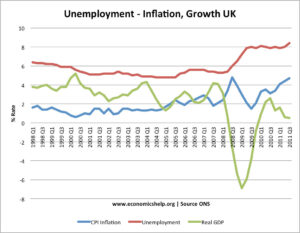
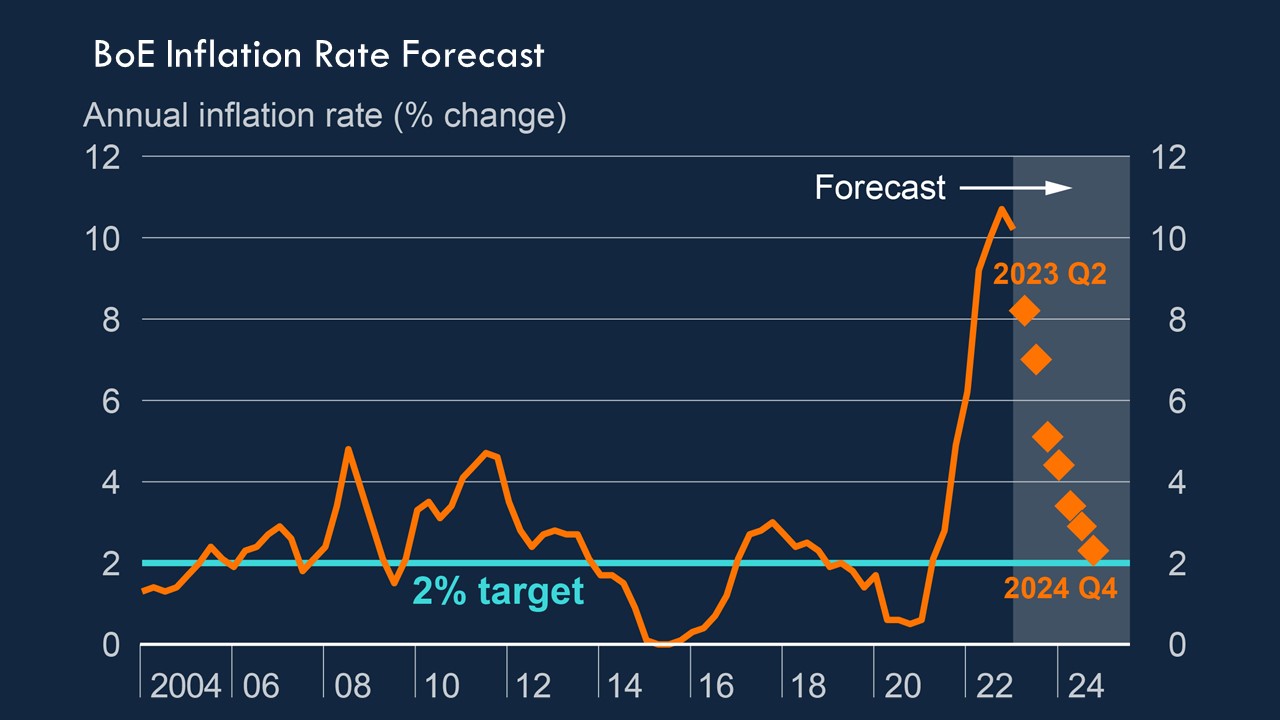
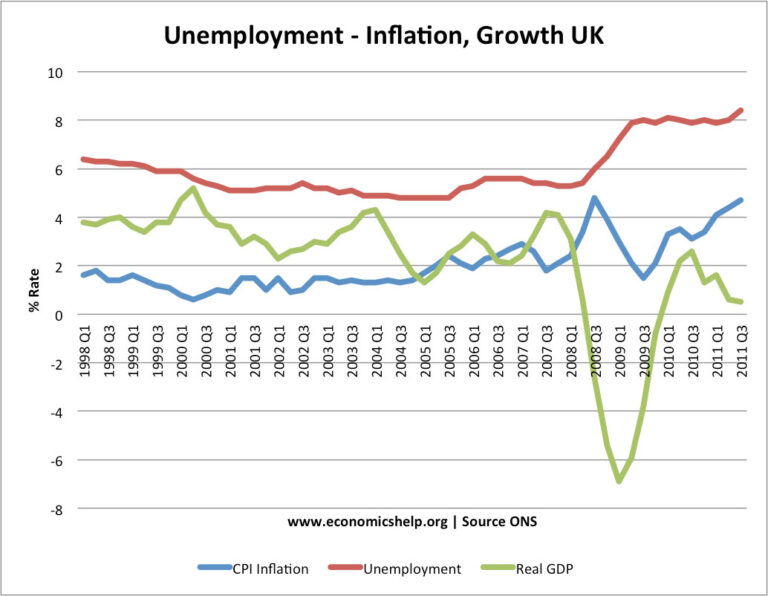
As of October 2023, the Bank of England has maintained its base rate at 5.25%, a figure reached following several adjustments in the past few years to combat rising inflation. The decision to hold the rate at this level comes amidst persistent inflationary trends, which peaked at nearly 8% earlier this year, significantly higher than the Bank’s target of 2%. The MPC’s stance is to balance the need to manage inflation while considering the impact on growth and employment.
The Global Context
The situation is not unique to the UK, as central banks worldwide are grappling with similar inflationary pressures. The US Federal Reserve recently raised its rates, and the European Central Bank has also been adjusting their rates to combat inflation. These global trends have implications for the UK economy, particularly in terms of exchange rates and foreign investments.
Implications for Borrowers and the Economy
For consumers, the base rate directly influences the interest rates on mortgages, personal loans, and savings accounts. A higher base rate tends to mean higher borrowing costs, potentially cooling consumer spending and impacting housing market dynamics. Conversely, savers may find better returns on savings accounts, allowing individuals and families to prepare for future financial goals.
Looking Ahead
Economists predict that the Bank of England may need to adjust the base rate further in the coming months, depending on inflation trends and economic recovery signs. If inflation shows signs of stabilising, a potential reduction in the base rate could be on the cards to stimulate growth. However, should inflation remain stubbornly high, the Bank might opt to raise the rate further.
Conclusion
The Bank of England base rate remains a vital tool in managing the UK economy. As the MPC continues to navigate challenging economic conditions, understanding the implications of the base rate is essential for consumers and businesses alike. Monitoring future changes will be crucial for anyone affected by borrowing and lending in the UK.