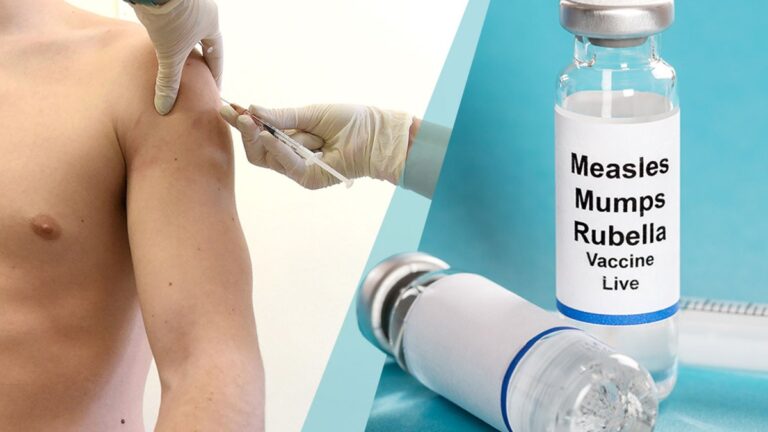
Introduction to Rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles, is a contagious viral infection that poses significant health risks, particularly to pregnant women and their unborn children. Recognising the symptoms and ensuring vaccination is crucial to preventing outbreaks and safeguarding public health.
What is Rubella?
Rubella is caused by the rubella virus and is typically characterised by a rash, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. The infection is generally mild in children; however, the implications for pregnant women can be severe, leading to congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) which can cause serious birth defects or miscarriage.
Current Statistics and Outbreaks
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), rubella remains a public health concern in countries where vaccination rates are low. In recent years, there have been sporadic outbreaks in regions that previously had high vaccination coverage, raising alarms amongst public health officials. In 2022, the WHO reported an increase in rubella cases in countries like Italy and Ukraine, highlighting the importance of maintaining high immunisation levels.
Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of rubella typically appear between 14 to 21 days after exposure to the virus and may include:
- Low-grade fever
- Rash that usually begins on the face and spreads
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Joint pain
- Cold-like symptoms such as a runny nose
Prevention Strategies
Vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent rubella. The MMR vaccine (measles, mumps, rubella) is recommended for children, usually administered at ages one and three. Health officials encourage ensuring that all eligible individuals are vaccinated, particularly women of childbearing age, to prevent the risk of CRS during pregnancies.
Conclusion: The Importance of Vaccination
The fight against rubella is ongoing, particularly as global health authorities strive to eliminate the virus entirely. Awareness and prevention through vaccination are essential steps in protecting individuals and communities. As outbreaks can have serious consequences, especially for pregnant women, maintaining high immunisation coverage is vital. For concerned parents and communities, staying informed and ensuring vaccinations are current is key to preventing future outbreaks of rubella.